Deterministic Chaos
6.D.3. Histograms of Orbits
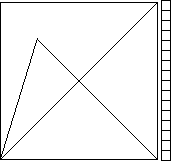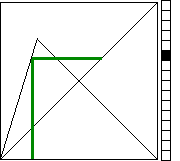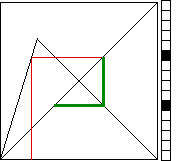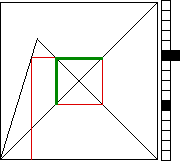
Following the graphical iteration
path, we see some
of the paths appear to run over the same lines. Often, this is the effect of the nonzero
width of pixels. Near enough numerical values can fall in the same pixel.
To keep track
of this, we plot the histogram of the iterates.
Divide the
vertical unit interval into some number of bins, one bin per pixel.
Then every time an xi lands in a bin, we increment the counter of the number of points that have
landed in that bin.
Visually, we represent this by plotting another pixel to the right.
|
| Click the picture to return. |
Here are some examples for the
logistic map L(x) = s*x*(1 - x). The
vertical gray band
separates the graphical iteration plot from the
histogram.
|
|
 |
| s = 0.9 After a few transients, the isolated hsitogram
points, the orbit approaches so near to the fixed point x = 0 that successive values fall in the
same pixel. Consequently, histogram is mostly a long horizontal line representing repeated values in
that pixel. |
|
Return to Deterministic Chaos.

